All organizational dysfunctions track directly to leadership failings (Part 3)
Ronald Sheckler • October 24, 2019
Threat spectrum revised: Violence is a distraction

The greatest differentiation for leadership quality and organizational effectiveness is approach to enterprise risk management. For optimal business resiliency it is necessarily an all-consequence effort. Any operational confusion poses distraction, ranging from minimum consequence and escalating to threaten enterprise viability. However, what do the seeming insignificant distractions mean? Is there more than simply the nuisance of noise and confusion for a “Day in the life…”?
For assessment and mitigation of hostile threats, expectations are for specific information of sponsor, method, and targets; absence of such is often used to delay or reject security related initiatives and limit funding. However, for virtual threats, emphasis is on identifying and reducing opportunities for intrusion with indifference to sponsor or motive. Network monitoring emphasizes detection and countering illicit access, including abuse of authorized-access. For external virtual threats, tactics/methods are necessarily shared across industry sectors because threat agility and incident volumes equate to a state of universal siege on information systems. Conversely, traditional physical security consulting often includes threat assessments extrapolated from collateral crime statistics, which are abstract and more obviously represent fear mongering for persuasion, relating to local personal safety and potential liabilities rather than coherent risk to an enterprise. Consequently, the essential significance and implication of these statistics is often unrealized. Three primary aspects of relevance apply: 1.Probability that a random incident may occur. 2. Any directly intentional threat may remain masked in the background noise, minimizing potential for detection and avoidance. 3. External emergency response capabilities may be limited and delayed as a result of collateral engagement, which extends necessity of self-reliance and increases due diligence liability.
The typical threat attribute that drives physical security investment is violence and its prevention at established operating locations. This begins with a spillover of domestic violence into the workplace, to active shooter, and because of international events, jumps to the severity of a coordinated terrorist attack, inclusive of various Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs). The after-effect of a violent incident is psychologically persistent and undermines staff productivity long after the event. Additionally, it infers significant liability upon the organization for safety and security due diligence. However, legitimate concerns for safety of staff and guests from potential violence within controlled spaces, eclipses significant vulnerabilities to enterprise viability from intentional exploitation of persons, while away, because of their corporate affiliation and specific knowledge.
Rethinking the threat spectrum, by including accidental and non-violent categories for balanced all-consequence mitigation, facilitates comprehensive review and assessment of human factors, as a contributor to enterprise vulnerability. Personnel performance is naturally variable but is also susceptible to influence. Social-Justice emphasis and advocacy for tolerance and accommodation of human frailties shifts the burden of personal choice and discretionary behavior consequences from the individual to the community and within business can create Collective Bargaining contention and sympathetic conflict with Human Resource management, which undermine essential discipline for adherence to policies and procedures. The factor that misleads perceptions for necessity is, in a stable public-safety/rule-of-law environment, an enterprise can be commercially competitive with mediocre effectiveness as an organization.
No criminals or terrorist were injured in the making of these images. However, the severity of direct and extended costs and consequence should be obvious. The associated confusion and distraction from unintentional human-factor incidents because of neglected incompetence or corruption, provides conditional vulnerability from increased exploitation opportunities that attract malicious threats.
Optimal business resiliency requires enlightened, empathetic, leadership that inspires individuals to dissociate personal distractions by establishing an organizational environment where policies evolve for relevance, comprehensive process/procedures are implemented with fidelity, and performance is motivated by satisfaction rather than job fear or duress.
SCHOFIELD'S DEFINITION OF DISCIPLINE. “The discipline which makes the soldiers of a free country reliable in battle is not to be gained by harsh or tyrannical treatment. On the contrary, such treatment is far more likely to destroy than to make an army”.
I am not suggesting that commercial organizations emulate military culture, which is more stereotype than reality. Discipline, in contrast to dogmatic contractual obedience, is a result that any organization or activity would benefit from because it is intrinsically self-aware and collaborative. Time, place, and purpose add legitimacy where non-conforming activity attracts scrutiny. However, as everyone pitches in to keep things in motion there is seldom time to scrutinize something out of place because lean operations and just-in-time supply chain management places emphasis on tight production schedules relative to staffing capacity. When success metrics default to fixate exclusively on production quotas, distractions become immediately corrected nuisances, rather than realized as indicators of potential threat.
Vulnerability is compounded by typical administrative constructs that segregate security into specialized physical and information technology categories. Physical intrusions and violence are traditionally actions managed by physical security specialists, with virtual network intrusions and data security aligned to information technology departments. Separation reduces coherence, creating blind-spots in vigilance and gaps in procedural controls. Additionally, countermeasures for unauthorized access, physical and virtual, emphasize external threats as most obviously consequential, however statistical data indicates higher incident rates and severity from internal access abuses. The segregation of physical security and information systems security is problematic as they are two dimensions of the same challenge and function optimally when synchronized, in a holistic design, around preserving critical functions and information essential to enterprise viability. It is important to realize that critical risk to the enterprise correlates to confident information controls. However, such programs traditionally focus on physical and virtual security for handling documents, media, electronic data archives, and associated networks in their principal location, but do not fully account for vulnerabilities when exploitation of persons occur outside the physical security perimeter of their primary workplace.
Risk evaluation is appropriately applied to all employees and associated entities with access to information and controlled space, but must also account for them as guest at external facilities or sponsored events. The global nature of commerce has staff routinely participating in activities and events away from their primary location and its associated security foot print. During these occasions they potentially expose their knowledge of corporate affairs and impose vulnerability upon the enterprise. The cumulative amount and significance of the information present within a group or at a particular event defines its attractiveness for exploitation. Again multiple independent threats may coincidentally target the same event for different motives. A day in the life of… may not be as thrilling as cinema but it is far noisier and challenging to sort out. For any event, threat attraction can be inferred by estimating value/consequence from direct loss of attendees and the information they possess as well as the liability implications to not provide for safety and security of staff and guests, as a host/sponsor. Understand that exploitation does not necessarily mean violent disruption of the event but the event creates a convenient consolidation for potential targeting of participants, individually or collectively, because it fixes their presence in an unfamiliar location where they may not recognize surveillance or threat indicators, unless specifically trained.
It is reasonable to expect that any course of action taken by a belligerent would be intentionally innocuous as it builds to culmination. This creates a challenge to situation awareness because threat actions, if suspected, may be confused with random criminal activity or social activism. Likewise, legitimate activities of labor, environmental, or human rights organizations may be unwittingly exploited to compliment or divert attention from a more divisive scheme that remains unrealized by civil authorities or security staff. This vulnerability, when assessed and viewed with a local or tactical perspective, ensures the tendency to over secure a site by creating and defending a strong point. As indicators support the conclusion of hostile interest, the immediate objective should be to inventory staff and information then modify security in a manner that prevents or restricts further collection of information so that attack opportunities are denied or delayed until counter-measures can be employed. However, is elevated security effectively extended beyond the formal venue and are personal behaviors undermining security efforts by wandering away from secure settings or by not communicating changes in location or coordinated itinerary? This is where procedural controls and personal discipline are essential to protecting both the individual and the enterprise.
Executive staff is routinely protected however, certain non-executive staff positions or incidental groupings of individuals achieve a special level of significance because the cumulative information they possess deserves special security consideration as an essential asset. Enterprise risk programs should proactively track and manage these exposures.
Consequence Criteria:
- Sensitive information, if disclosed would damage corporate operations within a state or province through the potential loss of product or staff and diminish corporate prestige at the local level.
- Protected information, if disclosed would cause serious damage to corporate operations across a country or geographic sub-region from the potential loss of infrastructure or capability and diminish corporate prestige at a national level.
- Guarded information, if disclosed would cause exceptional damage to the design and intentions of the corporation through the potential loss of pending litigation, market share, technology, or competitive advantage. Additionally, disclosure will diminish both the prestige and economic viability of the enterprise by providing cause for class action litigation or government action.
Target Susceptibility/Selection Criteria:
Who/Why:
The significance and consequently attractiveness of any individual, group, or event as a target must be continuously evaluated because it will change with the circumstances and dynamics of both business and regional politics. However, why can be more confidently determined and used to define a scope for program development.
Knowledge
- Business Plans
- Mergers and acquisitions
- Production details, partnerships, and modernizations
- Market analysis supporting operational decisions
Litigation/legal
- On-going liability (Corporate Defendant)
- Proposed (Corporate Plaintiff)
- Patent Applications
Technology
- Intellectual Property
- Access to corporate internal systems and spaces
- Access to corporate services subscriber/client information
Prominence
Wealth
Affiliation
How/Where:
Discerning the methods of how a threat may take action depends on a clear recognition of who is the threat and what is their intent. However, where can be more confidently anticipated because facilitated introspection will expose opportunities that enable threats to gain access and influence over persons that meet the criteria for an attractive target. This has implications for the selection and preparation of an event venue or rejecting a meeting or its suggested location as unsuitable because safety for personnel and control of information cannot be confidently established.
Typical defensive thought predisposes everyone to assume they are the intended target. Consequently emphasis is on countering direct threat actions. Additionally, discussions typically address singular events or one threat at a time, assuming emergency services are exclusively available. However, different threat motives will be attracted to different facets of an operation or activity and expectations should include that multiple threats may develop independently but manifest collaterally.
These inclinations represent the biggest fallacy in traditional security/risk planning and preparedness because an exploitation or attack may be motivated by the potential to indirectly gain access or influence over a third party. Appreciating the potential for indirect cause and effect will likewise enable a better appreciation of critical vulnerabilities that result from functional interdependencies.
The political and commercial significance of corporate activities within many countries routinely has prominent persons from outside of the organization present. This condition may attract and inadvertently introduce their uniquely associated threats into the situation to gain an exploitation opportunity. Detection signatures for third party threats may not conform to monitoring parameters, remaining unnoticed until post incident investigation makes them obvious.
Inevitably threat and target will meet. In some instances, threat proximity must be achieved for individuals, in others a device. Additionally, does threat intention or success require recovery/removal of an individual, device, or data? Concerns for operational simplicity will cause potential threats to first assess the static security profile for gaps/lapses. If necessary, a more sophisticated, coordinated action, incorporating cover and diversion will be considered; defensive actions drive threat evolution. An observable elevation in security profile may deter lesser threat actions but is seldom prepared for the level of sophistication it has inadvertently stimulated from a more determined threat. Additionally, violence potential is a distraction that generates alarmist tendencies, which must be managed so that an overzealous security profile or response escalation does not excessively restrict the essential activity it intends to protect?
Threat Spectrum, reevaluated:
- Espionage has the lowest probability for violence but the greatest potential for adverse impacts. Information advantages enable competitors to outpace targeted program objectives as well as disruption by provoking negative publicity or litigation. These activities are intentionally clandestine and seek long term financial benefits. They may range from a onetime elicitation opportunity during a conference to persistent leaks that continue because of monetary inducements and because the absence of overt violence keeps them beyond the attention of security or law enforcement (LE). The corporate identity is the reason for the attack and at the worst; consequences intend to adversely affect the entire enterprise. There is a wide range of motives for acquisition and exploitation of information, which include:
- Entities that want to out maneuver a competitor in order to win a service contract with the targeted entity.
- Entities that want to increase their position/value anticipating acquisition.
- Separating Employees seeking advantage in the job market.
- Information brokers that acquire and sell information of strategic business value about the targeted enterprise and its clients.
- Direct targeting by commercial business sector competitors.
- Direct targeting by nation state sponsored commercial competitors.
- Activism supporting a public or legal attack that may delay or undo business planning.
Studies have indicated that employees anticipating separation are inclined to abscond with information that they believe may be of value in securing their next employment. Pilfering information is seen as clean or benign and not easily proven or prosecutable, so there is reduced psychological deterrence than for traditional larceny. Additionally, there is still knowledge in their heads that is impossible to account for and control. Non-disclosures agreements are seldom enforced until after damage is done.
- Crime (Petty and Organized) increases the probability that localized violence will be a factor because expediency and intimidation are employed to prevent victims from taking effective action. These activities are typically covert and seek immediate or near term financial benefits by absconding with something of marketable value. This category of threat will target individuals for both the value of their personal assets as well as their corporate affiliation. Therefore, it is important for the corporation to internally determine the extent of their liability and obligation to pay for the safe return of any employee while on official travel as one factor in determining what ways and means are appropriate for establishing security in the first place.
- Terrorism is violence first. The political motives of terrorist often take resolution out of the hands of corporate leaders. The emotional nature of kidnappings, hostage killings, and potential use of explosives and mass effect weapons, means that any person or entity may be directly or indirectly affected. Sensational consequences intend to be undeniable. Attacks may have consequential spill over or compounded effects and force evacuation of nearby facilities or communities and delay resumption of operations within the affected area. This leads directly to a correlation between security preparedness and feasibility for business continuity of operations when one operation is disrupted by an attack against a neighbor. Recorded events for large industrial accidents best approximate what a terrorist attack may intend to create. However, unlike an accident, the determined nature of a politicized threat means that once committed to action something will occur. Currently it is the political /national affiliation of the corporate identity that determines attractiveness as a target and although, an attack may be devastating (loss of staff and facilities) within a local context, the long term effects are likewise localized to the area of the attack unless the corporate identity becomes the target motivating a systematic campaign directed across the enterprise.
- Natural Events are significant in the extent and duration that they may disrupt infrastructure and prevent resumption of operations in addition to the direct threat to personnel safety. The scale of some natural disasters, including pandemics, takes recovery out of the hands of corporate leaders and challenges the appropriateness of planning assumptions/provisions for business continuity. Terrorist hope to achieve the level of devastation witnessed during natural disasters but until that potential is reality, the review of these events is still the best way to evaluate scalable businesses resiliency and the potential success of business continuity preparedness for all hazards.
Threat Categories:
For optimal Enterprise Risk Management, another order of magnitude for analysis and planning integration is necessary. Deliberately expanding the scope of traditionally realized threats to include all consequences makes planning for mitigation and response more inclusive across enterprise leadership because it compliments operational efficiency studies and performance goals. Getting safety and security into routine, multi-echelon/multi-discipline management, discourse will be a significant improvement for most organizations.
Threat Categories:
1. Compliance Failure; is the most obvious category of threat, which is the basis for ubiquitous procedural controls. Consequence could be a fine or curtailment of operations resulting from an audit. Compliance standardization intends to establish a baseline practice that instead is often implemented as an achievement goal, which ultimately limits both investment and thoughts on the matter.
2. Accident; threats do not need to be malicious to impose significant consequence. Incidents are often linked to compliance violations compounding consequence. Therefore, accident prevention often becomes an item in managerial performance evaluations. However, accidental incidents are seldom reviewed for conditions which may be intentionally contrived.
3. Incompetence and Corruption; internal and external, here is where leadership is most critically influential; reducing undesirable human factors that impose both physical and psychological consequence on the enterprise. Internally, developing performance measures of effectiveness (PME) for critical tasks helps maintain efficiency and highlights priorities for staff training programs.
4. Business Sector Competitors; as a category includes both intentional actions by known entities and unintentional market turbulence that may cause key contractor/vendor businesses to fail, imposing consequence. Vendors and contractors may not be fully realized as essential and their business viability may fail independently of your contracted relationship.
5. Organized Crime; as a category is inclusive of all illicit maliciousness, from petty larceny to politicized hostilities (terrorism).
6. Civil Disruption; as a category is inclusive of labor strikes, targeted boycotts, and unrelated civil disruptions.
7. Severe Weather
and Natural Disaster; as a category includes pandemic.
Any assessment or survey determining exploitable vulnerability must consider, first and foremost, the susceptibility of the facility or activity to information collection. This includes information from direct observation as well as information disclosure resulting from the subject's operational practices. Additionally, every facility as well as the staff has identities in a local community. How much information is either in the public domain or filed and available through contractors or vendors? Consideration must also include casual discussions by employees away from work. Regardless of the sensitivity or location of a facility, it is erroneous to assume that information is not available or that it can be absolutely controlled. Therefore, the most significant realization available to security planners is to understand and accept the amount and nature of information available to anyone interested in investigating their site/operation.
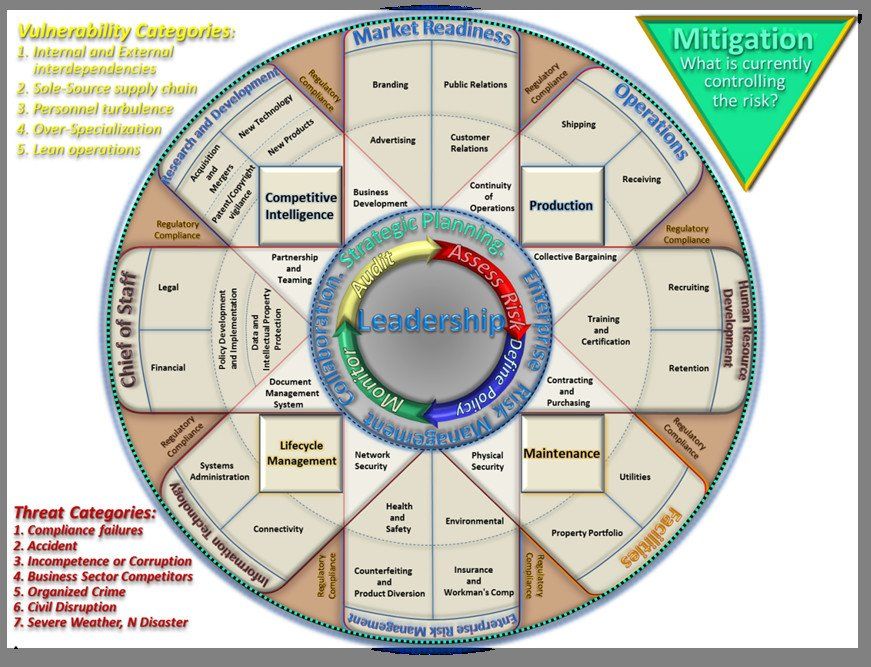
Administrative constructs will vary but, this graphic illustrates principal enterprise functions that all businesses evolve through, starting informally with a couple folks and a good idea, incrementally formalizing functions into a mature enterprise, which will be inevitably riddled with exploitable vulnerabilities.
Every task may be important to the person it is assigned to, because of personal performance evaluation, but not all routines are essential to enterprise viability. For differentiation, tasks that have a direct and immediate impact on internal productivity are considered essential; tasks that impose consequence on an external entity are critical. i.e customs declarations may be perceived as a simple clerical task but when values for quantity or country of origin are incorrect, the delay can have significant impact on downstream entities depending on delivery. All actions associated with the data entry on a customs form should be deliberately scrutinized and controls implemented to correct errors before the port of entry.
It does not matter how secure your network is if you can not retain talent and sensitive information walks out the door. An outstanding technician, in at start-up, may not have the skills or demeanor to effectively supervise persons as the organization grows, just because of seniority. Inappropriate lead or manager selection, often has a detrimental impact on an entire section, which compounds vulnerability because of reduced production and talent retention. Retaining talent must address multiple aspects of personal expectation and satisfaction. Do Performance Improvement Plans (PIP) as implemented, effectively remediate performance or is it a mechanism to avert termination recourse? Does the write-up on a PIP actually reveal a supervisor inadequacy? "At will" contract provisions reduce scrutiny of managerial competency.
Optimal risk reduction, especially for human factors, comes from diligent preparedness with relevant policies, comprehensive procedures, and disciplined behaviors. Redundant checks and balances for essential and critical tasks with responsive feedback loops for non-conforming activity are paramount. Know what is vital, be sure of your capabilities, strive to increase self-reliance, but know when and whom to ask for assistance then facilitate transition of incident control. Only enlightened leadership can move an enterprise beyond mediocre management effectiveness. When the full extent and potential of the organization is consistently accessed, vigilance need not be exhaustive nor preparedness burdensome and return on effort is resiliency providing agility, competitiveness, and profitability

Nařízení (EU) 2017/745 o zdravotnických prostředcích vstoupilo v platnost 26. května 2021. Platnost certifikátů vydaných podle stávajících směrnic vyprší nejpozději 24. května. Toto je třeba provést ve lhůtě, která odpovídá době nezbytné pro přezkoumání dokumentace a před vypršením platnosti současných certifikací. Česká republika stále nemá svůj oznámený subjekt. Jakmile dojde k akreditaci, bude ITC zavalen ohromným počtem nevyřízených podání v českém jazyce. Zajisdtěte si pomoc s podáním od týmu Arete-Zoe, který má s přípravou klinické dokumentace dle MDR bohaté zkušenosti.

The reduction of Czech-based Notified Bodies (NBs) leaves only one still pending accreditation and one in Slovakia that does accept submissions in Czech. The delay in accreditation has produced a significant backlog for submissions pending review and acceptance. The complexity of MDR is more stringent both for the preparers and the reviewers at the NB. This situation introduces many vulnerabilities into the submission process and represents substantial risk that can and should be minimized! The potential consequences of certification delays may be critical for some manufacturers. Is the cost penalty from delay because of necessary revision or rejection worth the minor economy of an in-house effort? Get your staff an assessment from a team with proven MDR success! Contact Arete-Zoe for a courtesy review of your situation and secure assistance that will reduce your risk! Stay agile, competitive, and profitable! What is the current situation? Regulation (EU) 2017/745 on medical devices (the Medical Device Regulation, MDR), which was adopted in April 2017, became applicable in the European Union on 26 May 2021, after a year delay due to Covid [i] . The certificates issued under the existing Directives for medical devices ( 93/42/EEC and 90/385/EEC ) will expire on or before May 24th, 2024. By then, all manufacturers who wish to keep their products on the market as medical devices, will have to upgrade their documents to the new standards. Previous documentation standards fall far short to the new requirements, placing significant burden on both the manufacturers and reviewers at the NB. Many previous submissions under MDR have been rejected based on documentation shortfalls within any of the many sections. When considered with the significant backlog, any aspect of documentation that requires revision only compounds certification delay and may jeopardize market access for many medical devices. All this needs to be done within a period that accounts for the time necessary for review prior to expiration of current certifications. Additionally, there is a significant bottleneck in submission processing due to the limited capacity of NBs in the EU due to a reduction in the number of designated NBs, increased number of products that are subject to review by NB due to reclassification, and increased complexity of MDR submissions compared to MDD/AIMD. The Czech Republic still does not have its own designated NB. Once accreditation occurs, the backlog of Czech language submissions will be overwhelming. The high number of returns and requests for amendments and revisions shall be expected in the initial months, slowing the process further for all. By May 2024, many manufacturers will find themselves in a situation when their products will no longer be marketable in the EU due to expired certificates and face additional consequences from having products purged from supply chain. Discussion MDR is here to stay. Czech Minister of Health MUDr. Vlastimil Válek in his introductory statement at the October 2022 AVDZP Conference [ii] stated that another postponement of MDR is out of question. While it is not in the interest of the European Union to be dominated by non-EU manufacturers, primarily from Asia, it is unlikely that the existing Regulation will be substantially changed to accommodate manufacturers’ concerns. Válek also reminded the public that the Wild East mentality with improvised devices throughout the hospital system that dominated the Czech market in the 1990s is gone and will not return. In short, MDR is a reality to which manufacturers will have to adjust. Notified bodies available to Czech manufacturers under MDR The number of EU NBs that are designated under MDR has increased to 34, half of which are located in Italy (9) and Germany (8). The remaining 17 are in Belgium (1), Croatia (1), Finland (2), France (1), Hungary (1), Ireland (1), the Netherlands (3), Norway (1), Poland (2), Slovakia (1), Slovenia (1), Spain (1) and Sweden (1) [iii] . European manufacturers can pursue certification of their products with any EU NB, with limitations to the type of product and the capacity and willingness of NBs to take on new clients. However, for access to the greatest number of NBs, the submission should be in English. Two Czech NBs were designated in Czechia under the 93/42/EEC (MDD): Institut pro testování a certifikaci, a.s. (ITC) and Elektrotechnický Zkušební Ústav, s.p. (EZÚ). Only one of them, ITC, is in the process for designation under MDR. However, the final scope of MDR codes ITC will be able to process has not been released. One additional institution, Czech Metrological Institute (CMI) is pursuing designation under MDR without prior history in medical devices under MDD or AIMD. The anticipated accreditation will take an additional year. Institut pro testování a certifikaci, a.s. (ITC), Czech Republic ITC’s current designations include Regulation (EU) 2016/425 Personal protective equipment, 2014/68/EU Pressure equipment, 2009/48/EC Safety of toys, Regulation (EU) No 305/2011 - Construction products and 2014/30/EU Electromagnetic compatibility. Designations under 93/42/EEC Medical devices and 98/79/EC In vitro diagnostic medical devices expired in May 2021 (MDD) and May 2022 (IVDD) [iv] . ITC will continue to perform audits under MDD during the transitional period until May 24, 2024. ITC submitted their application for designation under MDR on December 30, 2019. The Designating authority (ÚNMZ) verified completeness of the application and forwarded it to the European Commission in November 2020. The Commission designated the Joint Assessment Team in December 2020, which completed the evaluated in March 2021. On-site Joint Assessment was completed in June 2021. The official JAT report was issued in September 2021. ITC implemented CAPAs in fall 2021. In June 2022, designating authority ÚNMZ completed their review of CAPAs implemented by ITC and submitted it to the Joint Assessment Team for approval. In August 2022, ÚNMZ issued the final report. In September 2022, JAT issued its final assessment and a in October 23022, ITC underwent MDCG review and is now awaiting MDCG opinion that the notification can be accepted. The expectation is that ITC should be listed in the NANDO database by January 2023 for MDR [v] . According to Mgr. Jiří Heš, ITC will primarily serve Czech manufacturers who already are their clients and have certificates issued by them under MDD. New certificates under MDR won’t be issued in time and there will inevitably be a gap in coverage of products with valid MDD certification. [vi] ITC only began preparing application for designation under IVDR. Due to the extensive backlog of MDR certificates, it is reasonable to expect that the process of designation under IVDR will not be any faster. ITC currently does not offer any training on MDR for manufacturers or guidance on how to prepare submissions. The most significant thing any manufacturer can do for themselves is to ensure their submission is as appropriate as possible the first time. But they are left to their own means to sort out the transition from MDD to MDR. Without specific guidance from ITC on their expectations, there is significant risk from the ambiguity of the MDR Regulation itself. However, this risk can be reduced from experience from submissions under MDR to other NBs which will provide reasonable opportunity for a successful submission. Elektrotechnický Zkušební Ústav, s.p. (EZÚ), Czech Republic EZÚ’s current designations include Regulation (EU) No 305/2011 - Construction products and 2014/30/EU Electromagnetic compatibility. EZÚ won’t pursue designation under MDR. The activities EZÚ will continue include audit under MDD during the transitional period for 42 manufacturers whose certificates they serve, certification of quality management systems, and electrical safety. EZÚ also provides training on MDR for manufacturers and distributors [vii] . Czech Metrological Institute (CMI), Czech Republic CMI submitted their initial application in December 2020, a year later than ITC. The Joint Assessment Team evaluation (Article 39, paragraph 4 MDR) was completed in December 2021. In May 2022, CMI submitted their proposed CAPA plan. CMI strives to maintain the scope of devices included in their application (23 out of 44 basic codes and 18 out of 27 horizontal codes). The key requirement is to prove personnel availability for each code. CMI primarily intends to serve Czech manufacturers in Czech language, as only about a third of their reviewers have sufficient proficiency in English. CMI does not provide any training or guidance for manufacturers how to prepare documentation to pass their scrutiny. Certification of products on the Czech market There are over 400 Czech manufacturers listed in the database RZPRO holding nearly 6000 certificates that are currently valid. Of these, 4323 did not previously require the involvement of a NB (Class I). However, due to reclassification, some of these will require involvement of the NB under MDR, further stressing the throughput of the NB. Of the 1634 remaining certificates, 514 were issued by EZÚ and 391 by ITC. Another 133 MDD certificates were issued by other NBs that do not currently have MDR designation. The database also holds 2305 products other than Class I that do not have a NB listed. In total, ITC issued 541 certificates that are currently valid, including manufacturers from other countries. The database currently holds 630 valid certificates issued by EZÚ. All products certified by EZÚ will have to be recertified by another NB [viii] . The list of MDR codes that will be covered by ITC (or CMI, once designated) is not currently available. Mgr. Irena Storova (Czech State Institute for Drug Control) emphasized the quality of the MDR documentation as an essential condition required to avert a crisis. The current speed of issuing certificates by EU NBs is about 1.000 certificates a year. However, the anticipated need for medical devices in Europe is about 23.000 certificates issued by NBs over the period of 20 months, making the transition to MDR extremely challenging. The key problems are insufficient capacity of NB, partly due to accumulated backlog, partly due to increased complexity of MDR compared to MDD/AIMD, as well as inadequate preparedness of manufacturers to meet the new complex requirements of MDR [ix] . Experience of other EU NB shows exponential growth of applications and a serious lag in processing certificates. In February 2021, NBs received 1840 applications and processed 224 certificates. By October 2022, the number of applications grew to 8120, while the number of issued certificates was 1990 [x] . These numbers suggest further accumulation of backlog of unprocessed applications rather than catching up with the growing demand. The time to reach a Certificate according to MDR (MDR Quality Management System and Product certification) typically ranges from 13 to 18 months [xi] . This is consistent with ITC’s estimate that the review of a complete submission will take a year to issue a certificate. This means that all manufacturers who need their certificates renewed before the May 2024 deadline when they all expire will have to submit their applications before May 2023. Since ITC will only start accepting applications after the official MDR designation, it is safe to assume that all applications will be submitted in the period between the designation date and May 2023, creating a long backlog queue. To complicate the situation even further, manufacturers, whose MDR codes won’t be on ITC’s list, will have to look for a different NB to pursue their certificates. Czechia as a low price-point market The low-price level of devices on the Czech market complicates the transition to MDR even further. The system of defining reimbursements for medical devices is very rigid, and there are multiple pressures that keep prices down. These price controls conflict with increased costs associated with certification and recertification of products when considered with increased costs of energy, raw materials, transport, and labor. MUDr. Vlastimil Válek at the AVDZP Conference on October 13, 2022, stated that it is not in the interest of the European Union to allow non-EU manufacturers to dominate the EU market, and that there is an intrinsic value in self-sufficiency in times of crisis [xii] . The results from Survey on certifications and applications performed by MDCG & Stakeholders among NBs (51 NBs asked, 47 replies received) suggest that 60% of medical device clients are non-EU (10,913), compared to 7,143 EU clients [xiii] . Priority treatment for small business is not likely since SMEs are the majority of NB clients, both EU-wide and locally in the Czech Republic. In fact, as the threat for shortage of medical equipment becomes more urgent, policymakers might solve the crisis by prioritizing producers with high capacity, capable of meeting the demands of their respective health systems, as we have seen with the imports of medical equipment and protective materials during the Covid crisis. What is the risk to business due to delays in certification? The ability of NBs to process applications in a timely manner is an essential condition for the function of the medical device sector. This is directly influenced by the quality of manufacturers’ submission for certification. Manufacturers cannot legally keep their products on the EU market without valid certification. And, additional expenses will be incurred, if products have to be recovered from distribution chains due to delays in certification. Furthermore, this will create gaps in coverage, creating a void that can be filled by competitors. Extended periods of absence can stall otherwise good products and limit marketability once certification is finally obtained. Failure to obtain MDR certification for any portion of a product portfolio is an existential threat to any enterprise, potentially forcing reduction of staff, downsizing, making the enterprise vulnerable to competitors, or simply losing viability and going out of business. The absence of a feedback loop regarding the minutia of submissions’ content and format will cause additional delays and adjustments by the industry. ITC does not provide any MDR training and did not issue any guidance documents to facilitate successful submissions and reduce ambiguity relating to the novelty of the process. The first MDR certificate was issued in September 2019 by BSI [xiv] . This means that the cumulative experience in the industry among competition is significantly higher, placing Czech manufacturers 4 years behind other EU players. At present, Czech manufacturers have to rely on training provided by other NBs, industry consultants who rely on the same, in addition to feedback from their clients, and their own understanding of the Regulation and associated MDCG guidelines. Although CzechInvest does have a plan to start a comprehensive training program for manufacturers to facilitate the transition to MDR, the course has not started yet. The first students are expected to graduate in June 2024 [xv] . Learning curve by both newly designated NBs as well as manufacturers will inevitably affect the speed of processing, forcing reworks and amendments that would otherwise be avoidable. Securing consultancy with demonstrated MDR competency will remove substantial risk from the current situation. Recommendations What is the risk, and how does Arete-Zoe help your enterprise to mitigate such risk? The key to a successful MDR certification is a high quality, timely submission that complies with or better, exceeds minimum MDR requirements, ensuring timely processing and avoiding returns, requests for more information and outright rejections. It is important to note that the review and approval process depends on the understanding and application of MDR requirements by individual reviewers. Therefore, exceeding minimum requirements becomes a necessity for confident approval. The impact of additional information requests, although minor in terms of extra work, can be significant due to delays. Additionally, other manufacturers’ failed submissions in a long backlog of applications will continue to burden the system. The quality of the initial submission is essential to avoiding consequences in the transition to MDR and may be the single factor that keeps the business open. Manufacturers who have a fully trained in-house team already should still expect challenges in preparing MDR submissions themselves. The time to develop MDR expertise is very limited, considering the pressure to prepare the full documentation and submit it before May 2023. Even with a well-staffed team, the task can simply be overwhelming due to the sheer volume of material required in contrast to previous MDD/AIMD submissions. Arete-Zoe team has significant experience preparing clinical documentation for clients transitioning from MDD to MDR in both Czech and English and submissions through multiple NBs. Our exceptional success record with clinical documentation includes products that were previously rejected but passed with our assistance. We can help control the risk of failure or delay for our clients by providing the essential support you need to avert a avoidable delays in product certification. Arete-Zoe team can either prepare the full submission or augment your existing team with essential skillset your team might not have. References [i] https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/medical-device-regulation-comes-application [ii] Válek, V (2022). Introduction. AVDZP Conference 13/10/2022, Praha, Czech Republic. [iii] NANDO database https://ec.europa.eu/growth/tools-databases/nando/index.cfm?fuseaction=directive.notifiedbody&dir_id=34 [iv] NANDO database https://ec.europa.eu/growth/tools-databases/nando/index.cfm?fuseaction=directive.notifiedbody&dir_id=34 [v] Heš, J (2022). Implementace MDR: Kde jsme a kam směřujeme. AVDZP Conference 13/10/2022, Praha, Czech Republic. Institut pro Testování a Certifikaci. [vi] Heš, J (2022). Implementace MDR: Kde jsme a kam směřujeme. AVDZP Conference 13/10/2022, Praha, Czech Republic. Institut pro Testování a Certifikaci. [vii] Vlasák, M (2022). Dozorová činnost dle MDD. AVDZP Conference 13/10/2022, Praha, Czech Republic. Elektrotechnický zkušební ústav. [viii] Czech database of medical devices RZPRO https://eregpublicsecure.ksrzis.cz/Registr/RZPRO/ZdravotnickyProstredek [ix] Storova, I (2022). Problematika ukončení přechodného období MDR z pohledu SÚKL. AVDZP Conference 13/10/2022, Praha, Czech Republic. State Institute for Drug Control. [x] MDCG & Stakeholders (2022). Notified Bodies Survey on certyifications and applications (MDR/IVDR). 24/10/2022. European Commission. [xi] MDCG & Stakeholders (2022). Notified Bodies Survey on certyifications and applications (MDR/IVDR). 24/10/2022. European Commission. [xii] Válek, V (2022). Introduction. AVDZP Conference 13/10/2022, Praha, Czech Republic. [xiii] MDCG & Stakeholders (2022). Notified Bodies Survey on certifications and applications (MDR/IVDR). 24/10/2022. European Commission. https://health.ec.europa.eu/latest-updates/notified-bodies-survey-certifications-and-applications-2022-10-26_en?fbclid=IwAR3w3YH7UD2HBccQ6pBKWP3UlpgSnvQj9qFoNUeLIF-6ZWl8IOwP2Wx88Tk [xiv] BSI (2019). BSI certifies first product to the Medical Devices Regulation. 02 September 2019. BSI. https://www.bsigroup.com/en-GB/medical-devices/news-centre/enews/2019-news/bsi-certifies-first-product-to-the-medical-devices-regulation/ [xv] Hájek, J (2022). Národní plán obnovy. Komponenta 1. 4. Digitální ekonomika a společnost, inovativní start-upy a nové technologie. Program na podporu specifických systémových a produktových certifikací a souvisejícího vzdělávání. AVDZP Conference 13/10/2022, Praha, Czech Republic.

More than 500,000 medical technologies are available on the European market, from hospitals to community care settings and people's homes. The products range from syringes, pregnancy tests, and wheelchairs to X-Ray machines and body scanners, pacemakers, hip implants, and pharmacogenomic tests. The medical technology industry is the source of a constant flow of innovations. The sector spends about 8% of its sales on R&D. Typical product lifecycle is about 18 to 24 months when a new, improved version becomes available. In 2020, the European Patent Office (EPO) accepted nearly 14,200 patent applications in the medical technology sector, trumping pharmaceutical patents (8,500 applications) and biotechnology (7,200). European and U.S. entities filed almost 80% of the applications (38% EU and EEA, 39% U.S.) [ 1 ]. The European medical technology sector employs more than 760,000 people, mainly in Germany (210,000), the United Kingdom (102,800), Italy (94,000), France (89,000), Switzerland (63,000), and Ireland (40,000), accounting for 0.3% of total employment. In comparison, the European pharmaceutical industry employs around 795,000 people. These jobs reach a value-added of about €184,000 per employee. More than 33,000 medical technology exist in Europe, of which 95% qualify as small, medium, and micro-sized companies (SMEs). The majority of these enterprises employ less than 50 people [ 1 ]. In 2020, Europe had a positive trade balance in the medical technology sector of € 8.7 billion. Compared to 2019, the European trade balance dropped by 27.5% (€ 12 billion in 2019). The most important trading partners for Europe are the United States, China, Japan, and Mexico. Germany, Ireland, the Netherlands, Belgium, and Switzerland have the highest trade share, both within and outside the EU [ 2 ]. Until May 2021, the medical device sector was regulated by Medical Device and In Vitro Diagnostic Device Directives 93/42/EC and 90/385/EEC (MDD and IVDD), when the new Regulations replaced these: Medical Device Regulation (EU) 2017/745 (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Device Regulation (IVDR) 2017/746 [ 3 ],[ 4 ]. The new regulations introduced numerous changes, including the reclassification of some devices, requiring additional obligations for manufacturers to comply with. About 85% of in-vitro diagnostic devices will now require Notified Body involvement, compared to ~20% under the IVDD. Existing MDD/IVDD certificates remain valid until May 2024. After this date, all devices on the EU market must comply with the new MDR/IVDR regulations [ 5 ]. For some manufacturers, the costs associated with keeping some of their devices on the market under MDR/IVDR may no longer justify the expense considering their profitability. Others may not be able to obtain new CE Mark certification in time due to decreased capacity of notified bodies. These factors combined are already reducing the number of devices on the EU market and limiting the certification of innovative products. The number of notified bodies available to review new certifications and recertifications dropped significantly under the MDR/IVDR. Of 51 notified bodies designated to MDD [ 6 ] and ten to AIMDD [ 7 ], only 29 obtained designation for MDR, of which seven operate in Germany, seven in Italy, and three in the Netherlands [ 8 ].

The Medical Device industry produces a vast number of products, ranging from bandages and surgical instruments to life function monitors to imaging technology. The technology currently in use varies from devices that have been in use for decades to highly innovative products. Innovations in the medical device field are frequent and typically incremental in response to feedback from physicians. Mordor Intelligence estimated the global Medical Devices market at USD 532.62 billion in 2021, growing at a CAGR of around 5.5%, to reach USD 734.39 billion in 2027 [1]. Fortune Business Insights projects the global medical devices market growth from $455.34 billion in 2021 to $657.98 billion in 2028 at a CAGR of 5.4%. This development follows a decline from 2020, when CAGR dropped to 3.7% due to the pandemic [2]. The key drivers of market growth include the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, increased disability throughout the population, technological advancements in medical devices, and population aging. The U.S. medical device market was valued at USD 186.5 billion in 2021 and is anticipated to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.0% over the forecast period to reach USD 262.4 billion in 2028 [4]. The Medical Device sector is even larger than Biopharmaceuticals, that by comparison, employed over 224,000 people, earning $21.2 billion [3]. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the increasing geriatric population in the country are the key market drivers. The Medical Device industry has a significant impact on the U.S. economy and supports hundreds of thousands of jobs. More than 80 percent of U.S. medical device companies have fewer than 100 employees [5]. In 2020, the U.S. Medical Device industry supported over 329,000 jobs, with an annual payroll of $25.8 billion [3]. Employment and payroll for Medical Device Subsectors, 2020 ( SelectUSA ):

In the high consequence environment of pharmaceutical development, any assumption made earlier in the process can prove extremely costly if uncorrected once more information becomes available. From a business perspective, it is essential to create a safe avenue for communication of concerns regarding the drug candidate’s efficacy, safety, toxicity, or pharmacological function immediately as the researchers become aware of them.

Innovation always involves the risk of failure. It is an art to see what the data show, and what they don't, and which projections are the result of our wishful thinking or unsubstantiated assumptions. It may be just my impression that 14th-century logician William of Ockham whispers in my ear that entities shall not be multiplied unnecessarily.

Companies are growing in size due to acquisitions and mergers. Operations routinely span across geographical, jurisdictional, and cultural boundaries. The trend of industry consolidation continues in 2015 and 2016: the total number of deals flattened and remained even at around 600 mergers a year. Geographically, mergers, and acquisitions have been shifting from the U.S. to Western Europe. This shift is the result of transactions driven by the need to add complementary products to the core business areas and tax inversions.